Minikube is a free open-source solution that creates a single node Kubernetes cluster [Link]. See also the official documentation at [Link].
With a single combined Master+Worker node one can develop, test, or simulate a K8s infrastructure.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y sudo apt install nano htop wget curl apt-transport-https -y [ -f /var/run/reboot-required ] && sudo reboot -f
No matter if the Minikube is installed in a virtual or in a physical machine, it will need to virtualize the cluster using VirtualBox, KVM, or even Docker:
Installing VirtualBox (if this is your preference)
sudo apt install virtualbox virtualbox-ext-pack -y
Installing KVM (if this is your preference)
sudo apt install qemu-kvm libvirt-dev bridge-utils libvirt-daemon-system libvirt-daemon virtinst bridge-utils libosinfo-bin libguestfs-tools virt-top -y sudo modprobe vhost_net echo "vhost_net" | sudo tee -a /etc/modules
Installing Docker (recommended)
sudo apt install docker.io -y
Remember to use the Docker driver and set as the default one. The running user must be part of the docker group:
minikube start --driver=docker minikube config set driver docker
NESTED VIRTUALIZATION FOR PROXMOX
If you are running in Proxmox, certify your bare-metal hypervisor has enable nested support or the start of the Minikube will fail:
cat /sys/module/kvm_intel/parameters/nested
If outputs Y, it is all good. If outputs N follow the next steps:
echo "options kvm-intel nested=Y" > /etc/modprobe.d/kvm-intel.conf echo "options kvm-amd nested=1" > /etc/modprobe.d/kvm-amd.conf modprobe -r kvm_intel modprobe kvm_intel cat /sys/module/kvm_intel/parameters/nested
Note: replace kvm_intel with kvm_amd for for ADM hardware.
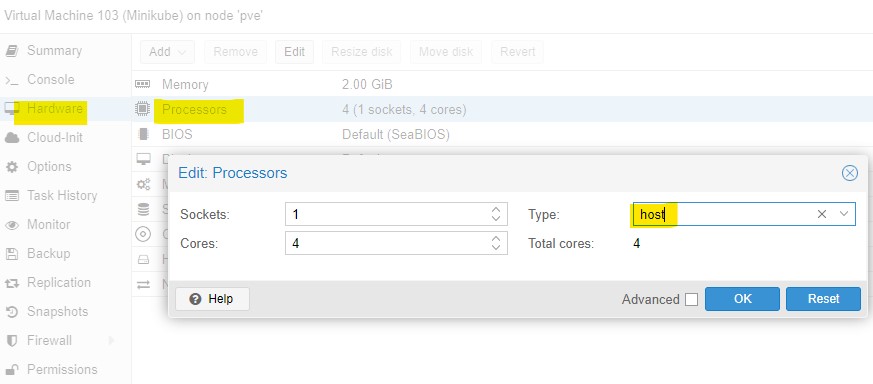
Also configure the guest VM processors type to host:
INSTALLATION
Minikube
wget https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-linux-amd64 chmod +x minikube-linux-amd64 sudo mv minikube-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/minikube minikube version minikube --help
Kubectl
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/`curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt`/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl chmod +x kubectl sudo mv kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl kubectl version --short
AUTO-START MINIKUBE ON BOOT
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/minikube.service
[Unit] Description=minikube [Service] Type=oneshot RemainAfterExit=yes User=USERNAME ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/minikube start --driver=docker ExecStop=/usr/local/bin/minikube stop [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl enable minikube
MINIKUBE CHEATSHEET
- minikube start
- Start or deploy a new cluster.
- minikube stop
- Stop the existent cluster.
- minikube pause
- Pause the cluster.
- minikube unpause
- Resume the cluster.
- minikube status
- Check the status of Minikube.
- minikube delete
- Destroy the existent cluster.
- minikube ssh
- Attach the current terminal to the cluster.
- minikube logs
- Watch the logs.
- minikube addons list
- Lists enabled and disabled addons.
- minikube addons enable dashboard
- Enables an addon.
- minikube start –addons dashboard
- Starts addons on system start up.
- minikube dashboard –url
- Gets the URL to the dashboard that can be accessed from local host on a random port (http://127.0.0.1:34005/api/v1/namespaces/kubernetes-dashboard/services/http:kubernetes-dashboard:/proxy/).
- minikube addons enable ingress
- Enables the out-of-the-box NGINX Ingress Crontoller.
Create the following resource to make the Dashboard always accessible through the address kubernetes.local (remember to add it to your hosts file):
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: kubernetes-dashboard-ingress
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: "/"
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
- host: kubernetes.local
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: kubernetes-dashboard
port:
number: 80
KUBECTL CHEATSHEET
Create the alias for easier usage:
alias k="minikube kubectl --"
- k cluster-info
- k config view
- k get nodes
- k get pods
- k get deployments
- k get events
- k proxy –address=’0.0.0.0′ –disable-filter=true
- Makes the dashboard accessible from outside the host on port 8001 (http://10.10.10.10:8001/api/v1/namespaces/kubernetes-dashboard/services/http:kubernetes-dashboard:/proxy/).
OTHER POSTS
K3s on Ubuntu 22.04 [Link].
MicroK8s on Ubuntu 22.04 [Link].
K8s Persistent Volumes [Link].
K8s Cheat Sheet [Link].
K8s Dashboard [Link].