
MicroK8s is the Canonical single-package fully conformant lightweight Kubernetes [Link]. It means, it is a 100% compatible Kubernetes orchestrator that can be deployed with a “single-click” on Ubuntu and many other distributions via Snap.
When compared with MiniKube [Link] and K3s [Link], MicroK8s is a minimal production Kubernetes that offers with the minimal effort for operating (low-ops).
Kubernetes is a beast created by Google to meet Google needs of scalability, that is why it is a common knowledge that Kubernetes is Hard to deploy and manage. This makes many companies opt for managed services such as EKS (from AWS), GKE (from GCP), or AKS (from Azure). And that comes with an associated price tag.
Most of the use cases for orchestrating clusters of containers are very simple and MicroK8s suits these requirements by far.
INSTALLATION
sudo snap install microk8s --classic microk8s.inspect
That is it! Even kubectl is included in the package.
To use MicroK8s without sudo,add your username to the microk8s group.
sudo usermod -a -G microk8s userName
Stopping and starting the MicroK8s Deamon.
microk8s.stop microk8s.start
BASIC COMMANDS
sudo microk8s kubectl get nodes sudo microk8s kubectl get services
To avoid repetition, here is another post that show cases standard Kubernetes commands and use cases [Link].
EXTENDED FEATURES
Enabling popular Addons.
sudo microk8s enable dashboard sudo microk8s enable registry sudo microk8s enable ingress sudo microk8s enable dns sudo microk8s enable gpu sudo microk8s enable ha-cluster sudo microk8s enable cert-manager sudo microk8s enable prometheus sudo microk8s enable community sudo microk8s enable istio
ACCESSING THE DASHBOARD
sudo microk8s enable dashboard sudo microk8s kubectl create token default
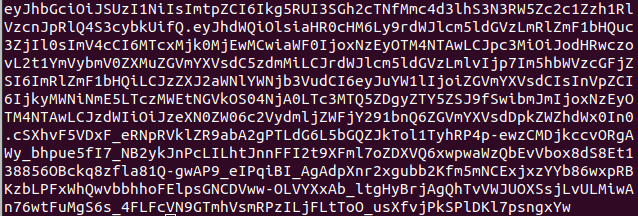
By default, the token expires in 1 hour. If necessary, give it more time or add the namespace:
sudo microk8s kubectl create token default --namespace=namespace --duration=24h
Now, expose the dashboard.
sudo microk8s kubectl port-forward -n kube-system service/kubernetes-dashboard 10443:443
Navigate to https://127.0.0.1:10443 and paste generated token:
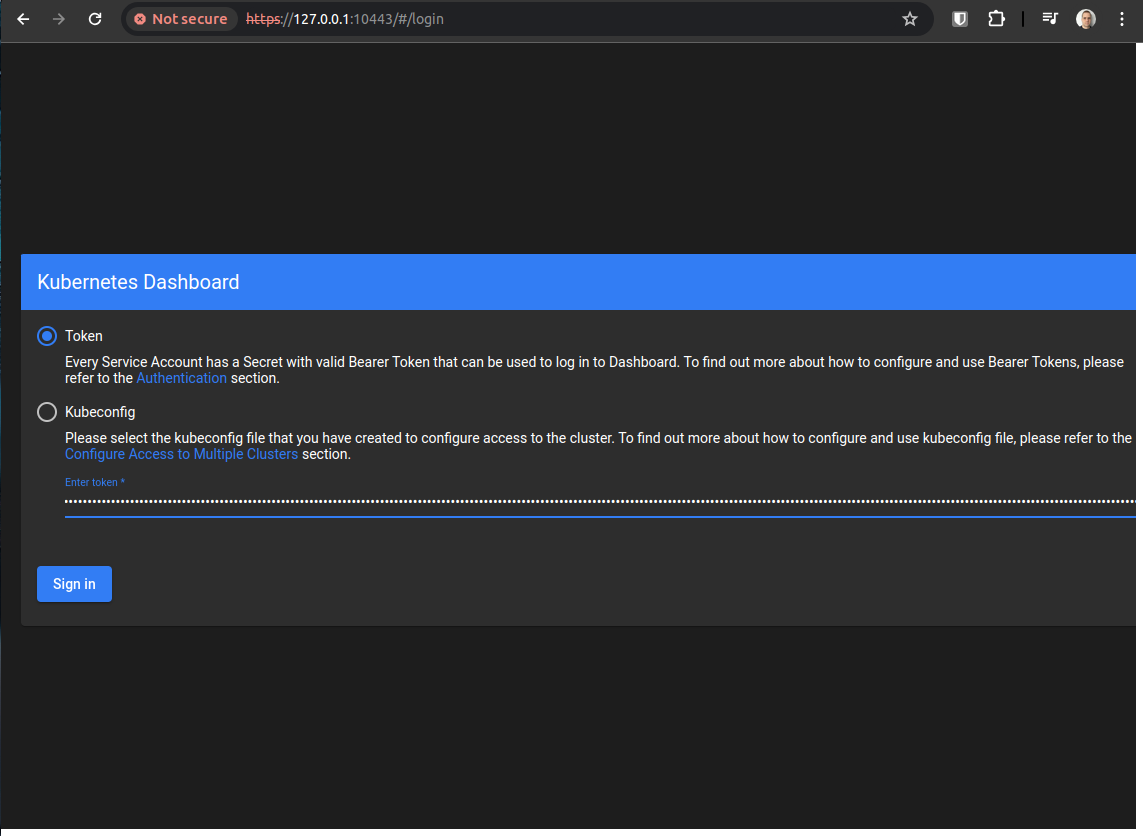
Note: this dashboard is not specific from MicroK8s. Instead, it is a Kubernetes module and is not in the scope of this post to walk-through the Dashboard. Check our the Dashboard Walk-through post at [Link].
RUNNING MICROK8S IN PROXMOX LXC
Create a new CT and uncheck the option for “unprivileged”.
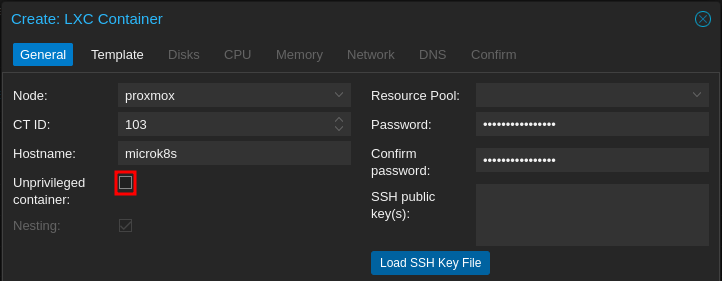
Before starting the CT for the first time, on open a shell on the host and edit the CT configuration file.
nano /etc/pve/nodes/proxmox/lxc/100.conf
lxc.apparmor.profile: unconfined lxc.cap.drop: lxc.mount.auto: proc:rw sys:rw lxc.mount.entry: /dev/fuse dev/fuse none bind,create=file 0 0 lxc.mount.entry: /sys/kernel/security sys/kernel/security none bind,create=file 0 0
Then, start the CT and add the following line to the crontab of the root user.
crontab -e
@reboot ln -s /dev/console /dev/kmsg
Setup the environment.
ln -s /dev/console /dev/kmsg apt update && apt upgrade -y apt install snapd squashfuse fuse -y reboot
Now, the installation can happen.
snap install microk8s --classic apparmor_parser --add /var/lib/snapd/apparmor/profiles/snap.microk8s.* microk8s.inspect reboot
After rebooting, check if it is still working as expected.
microk8s.inspect microk8s kubectl get nodes microk8s kubectl get services
BONUS
Auto-start Microk8s and it’s the dashboard on startup.
nano /etc/systemd/system/kubectl.service
[Unit] Description=Port forward for Kubernetes Dashboard After=network.target [Service] ExecStart=/root/microk8s.sh Restart=always User=root [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
nano /root/microk8s.sh chmod +x /root/microk8s.sh
#!/bin/bash apparmor_parser --add /var/lib/snapd/apparmor/profiles/snap.microk8s.* microk8s.start sleep 30 /snap/bin/microk8s kubectl port-forward -n kube-system service/kubernetes-dashboard 10443:443 --address 0.0.0.0
systemctl daemon-reload systemctl enable kubectl --now
OTHER POSTS
Minikube on Ubuntu 22.04 [Link].
K3s on Ubuntu 22.04 [Link].
K8s Persistent Volumes [Link].
K8s Cheat Sheet [Link].
K8s Dashboard [Link].