OSPF is one open standard (no proprietary) routing protocol. It is a link-state protocol and allows all the routers on the network to map the whole network to make its own decisions based on the big print.
Given the scenario below, PC1 needs to reach PC2:
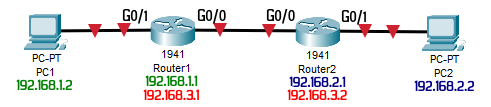
Router1
enable configure terminal no ip domain lookup line con 0 logging synchronous hostname Router1
interface g0/0 ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.252 no shutdown interface g0/1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown
Router2
enable configure terminal no ip domain lookup line con 0 logging synchronous hostname Router2
interface g0/0 ip address 192.168.3.2 255.255.255.252 no shutdown interface g0/1 ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown
Example of a Single Area configuration:
Router1
router ospf 1 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/1
Router2
router ospf 1 network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/1
For simple networks with few routers it works perfectly. The problem start when there are many routers, let’s say 50. When one link goes down all the routers start to change list state messages and this could be avoided be segmenting the network in zones:
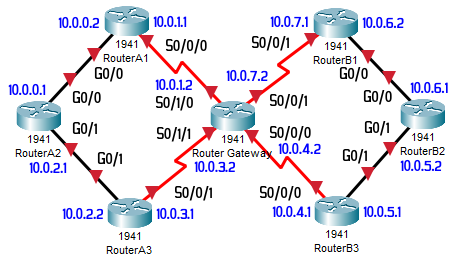
Configuring the Interfaces according to the diagram above:
RouterA1
enable configure terminal hostname RA1 no ip domain lookup line con 0 logging synchronous interface g0/0 ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.0 no shutdown interface s0/0/0 ip address 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown
RouterA3
enable configure terminal hostname RA3 no ip domain lookup line con 0 logging synchronous interface s0/0/1 ip address 10.0.3.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown interface g0/1 ip address 10.0.2.2 255.255.255.0 no shutdown
RouterB2
enable configure terminal hostname RB2 no ip domain lookup line con 0 logging synchronous interface g0/0 ip address 10.0.6.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown interface g0/1 ip address 10.0.5.2 255.255.255.0 no shutdown
Router Gateway
enable configure terminal hostname Gateway no ip domain lookup line con 0 logging synchronous interface s0/0/0 ip address 10.0.4.2 255.255.255.0 no shutdown interface s0/0/1 ip address 10.0.7.2 255.255.255.0 no shutdown interface s0/1/0 ip address 10.0.1.2 255.255.255.0 no shutdown interface s0/1/1 ip address 10.0.3.2 255.255.255.0 no shutdown
RouterA2
enable configure terminal hostname RA2 no ip domain lookup line con 0 logging synchronous interface g0/0 ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown interface g0/1 ip address 10.0.2.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown
RouterB1
enable configure terminal hostname RB1 no ip domain lookup line con 0 logging synchronous interface g0/0 ip address 10.0.6.2 255.255.255.0 no shutdown interface s0/0/1 ip address 10.0.7.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown
RouterB3
enable configure terminal hostname RB3 no ip domain lookup line con 0 logging synchronous interface s0/0/0 ip address 10.0.4.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown interface g0/1 ip address 10.0.5.1 255.255.255.0 no shutdown
Configuring the OSPF according to the Areas on the diagram:
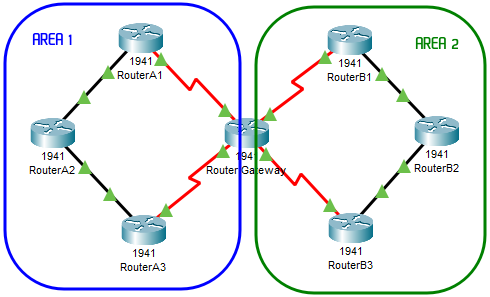
RouterA1
router ospf 1 network 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 1 network 10.0.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
RouterA2
router ospf 1 network 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 1 network 10.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
RouterA3
router ospf 1 network 10.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 1 network 10.0.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
Router Gateway
router ospf 1 network 10.0.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 1 network 10.0.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 1 network 10.0.7.0 0.0.0.255 area 2 network 10.0.4.0 0.0.0.255 area 2
RouterB1
router ospf 1 network 10.0.7.0 0.0.0.255 area 2 network 10.0.6.0 0.0.0.255 area 2
RouterB2
router ospf 1 network 10.0.6.0 0.0.0.255 area 2 network 10.0.5.0 0.0.0.255 area 2
RouterB3
router ospf 1 network 10.0.5.0 0.0.0.255 area 2 network 10.0.4.0 0.0.0.255 area 2
Note:
- Routers A* are area 1, so they are colled Internal;
- Routers B* are area 2, so they are colled Internal;
- Router Gateway has interfaces in area 1 and area 2, so it is called Area Border or Backbone;
The router gateway to outside the network has to have this config:
router ospf 1 default-information originate ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 g0/0
This will inform all the other routers who of them is the ‘gateway of last resort‘ when one network is unknown.
To check the configuration in each Router issue the commands:
show ip route show ip route ospf show ip protocols show ip interface brief show ip ospf show ip ospf interface brief show ip ospf interface show ip ospf neighbor show ip ospf database
Reference Bandwidth (for optimized route calculation):
router ospf 1 auto-cost reference-bandwidth 10000 ip ospf cost 22222
Set all interfaces as Passive by Default:
passive-interface default no passive-interface Serial0/0/0 no passive-interface Serial0/0/1
To apply authentication to join the OSPF, issue the same command in all interfaces in all routers:
ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 PASSWORD ip ospf authentication message-digest
Remember to replace ‘PASSWORD’ with one secret of your choice.
Learn more about [OSPF Single – CertBros]
Learn more about [OSPF Multi – CertBros]
The preview Post was about RIPv2 [Read It].
The following Post is about EIGRP [Read It].