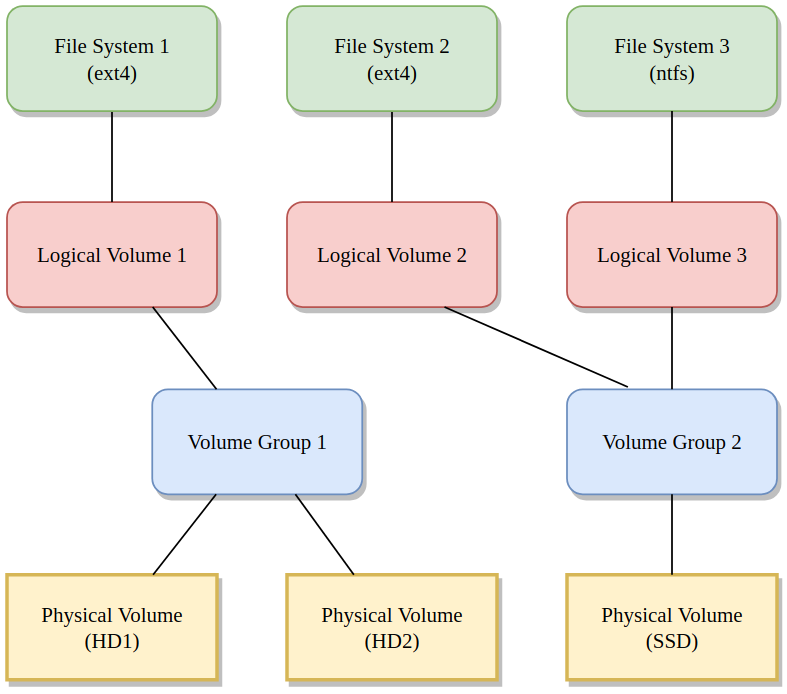
Logical Volume Management (LVM) is a method of space allocating on mass-storage devices.
It can provide superior features to the traditional partitioning schema such as concatenating, striping or combining partitions, re-sizing or moving partitions, potentially without rebooting.
Some related commands that will help with the LVM commands are:
lsblk blkid /dev/mapper/lg_name-lv_name
Displaying information:
pvdisplay vgdisplay lvdisplay lvs
Claiming a new Physical device to extend an existent Logical Volume:
pvcreate /dev/sdb vgextend vg_name /dev/sdb lvextend -L +5G /dev/mapper/lg_name-lv_name resize2fs /dev/mapper/lg_name-lv_name
Extending an existing Logical Volume to the whole extension of the Logical Group:
lvextend --resizefs -l +100%FREE /dev/mapper/lg_name-lv_name
Creating new Logical Volumes on the same new Volume Group:
vgcreate vg2_name /dev/sdc lvcreate vg2_name -L 10G -n lv2_name mkfs.ext4 /dev/mapper/vg2_name-lv2_name lvcreate vg2_name -L 10G -n lv3_name mkfs.ext4 /dev/mapper/vg2_name-lv3_name
lvcreate /dev/mapper/vg2_name-lv3_name -L 5G -s -n lv3_snapshot mount /dev/mapper/vg2_name-lv3_snapshot /mount_point/ lvconvert --merge /dev/mapper/vg2_name-lv3_snapshot lvchange -an /dev/mapper/vg2_name-lv3_name lvchange -ay /dev/mapper/vg2_name-lv3_name