Python is a versatile and human friendly script language that among the most popular ones.
Its potential is virtually unlimited when considered the vast amount of libraries freely available in packed managers such as PIP.
Index of tricks in this post:
- Creating QR Codes
- Removing Background from Images
- HTTP connections via Tor (Darkweb)
- Easy Graphic User Interface (GUI)
CREATING QR CODES
Install the dependency called segno:
pip install segno
Now, the library (segno) can be imported and used in your code:
import segno
qrcode = segno.make("Text to be encoded")
qrcode.save("fileName.png", dark="darkblue", light="white", border=5, scale=10)
qrcode.save("fileName.png", dark="darkblue", light=None, scale=10)
qrcode.terminal()


For RGB with Alpha Transparency 8-digit notation:
qrcode.save("fileName.png", dark="ff000080", scale=10)
 ,
,
Note: in the RGBA 8-digit notation, the first 6-digts represents the RGB (from 000000 to FFFFFF) plus 2-digits for the transparency (from 00 to FF, where 00 means no transparency and FF means full transparency). See more colorful notations at Segno documentation [Link].
List of popular output formats (serializers):
- PNG
- Image with transparency.
- SVG
- Vetorized image with transprency.
- TXT
- No color or transparency supported.
- PDF
- Transparency not supported.
- Streams/Buffers
- Capable of streaming the output to a stream/buffer
Outputting to a buffer (read more at [Link]):
import segno
import io
qrcode = segno.make("Text to be encoded")
buffer = io.BytesIO()
qrcode.save(buffer, kind='png')
print(buffer.getvalue())
API Endpoint / HTTP Server that will respond with a QR Code:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from http.server import SimpleHTTPRequestHandler
from socketserver import TCPServer
from urllib.parse import unquote
import segno
import io
def http_server(host_port):
class CustomHandler(SimpleHTTPRequestHandler):
def do_GET(self) -> None:
def send_200(content_type="application/json"):
self.send_response(200)
self.send_header("Content-type", content_type)
self.send_header("Cache-Control", 'no-cache, no-store, must-revalidate')
self.send_header("Pragma", 'no-cache')
self.send_header("Expires", '0')
self.end_headers()
self.path = unquote(self.path)
if self.path == '/' or self.path == '/qrcode.png':
if self.path == '/':
send_200('text/html')
self.wfile.write(bytes(' ', 'utf-8'))
elif self.path == '/qrcode.png':
send_200('image/jpeg')
qrcode = segno.make("Text to be encoded")
buffer = io.BytesIO()
qrcode.save(buffer, kind='png', scale=10)
self.wfile.write(bytes(buffer.getvalue()))
else:
return
return
else:
self.send_response(404)
self.end_headers()
return
class _TCPServer(TCPServer):
allow_reuse_address = True
httpd = _TCPServer(host_port, CustomHandler)
httpd.serve_forever()
try:
http_server(('0.0.0.0',8080))
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print(' Interrupted')
exit()
', 'utf-8'))
elif self.path == '/qrcode.png':
send_200('image/jpeg')
qrcode = segno.make("Text to be encoded")
buffer = io.BytesIO()
qrcode.save(buffer, kind='png', scale=10)
self.wfile.write(bytes(buffer.getvalue()))
else:
return
return
else:
self.send_response(404)
self.end_headers()
return
class _TCPServer(TCPServer):
allow_reuse_address = True
httpd = _TCPServer(host_port, CustomHandler)
httpd.serve_forever()
try:
http_server(('0.0.0.0',8080))
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print(' Interrupted')
exit()
Navigate to the following address using your browser:
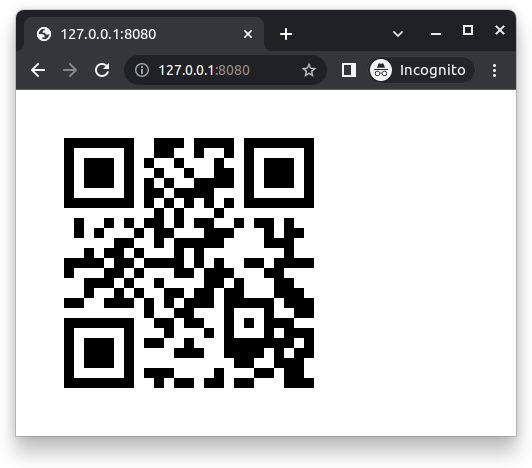
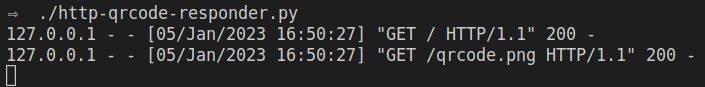
On the terminal, the API will log both requests:
REMOVING BACKGROUND FROM IMAGES
pip install rembg
OR (for GPU support)
pip install rembg[gpu]
Create the file rembg-app.py with the following content:
#!/usr/bin/python3
from rembg import remove
import sys
input_path = sys.argv[1]
output_path = sys.argv[2]
with open(input_path, 'rb') as i:
with open(output_path, 'wb') as o:
input = i.read()
output = remove(input)
o.write(output)
Make the script executable and call it as follows:
chmod +x rembg-app.py ./rembg-app.py input.png output.png
Alternatively, the following code generates the same result with a simplified logic:
from rembg import remove from PIL import Image input_path = 'input.png' output_path = 'output.png' input = Image.open(input_path) output = remove(input) output.save(output_path)
Note: the module rembg can be called directly from the command line. rembg i input.png output.png, for a local file, rembg p input_dir output_dir for a local directory, or curl -s http://example.com/input.png | rembg i > output.png for piping a remote file. If started as an HTTP server (rembg s) and be called via curl "http://localhost:5000/?url=https://example.com/input.png" > output.png
While some objects are not properly recognised, most are impressively extracted:
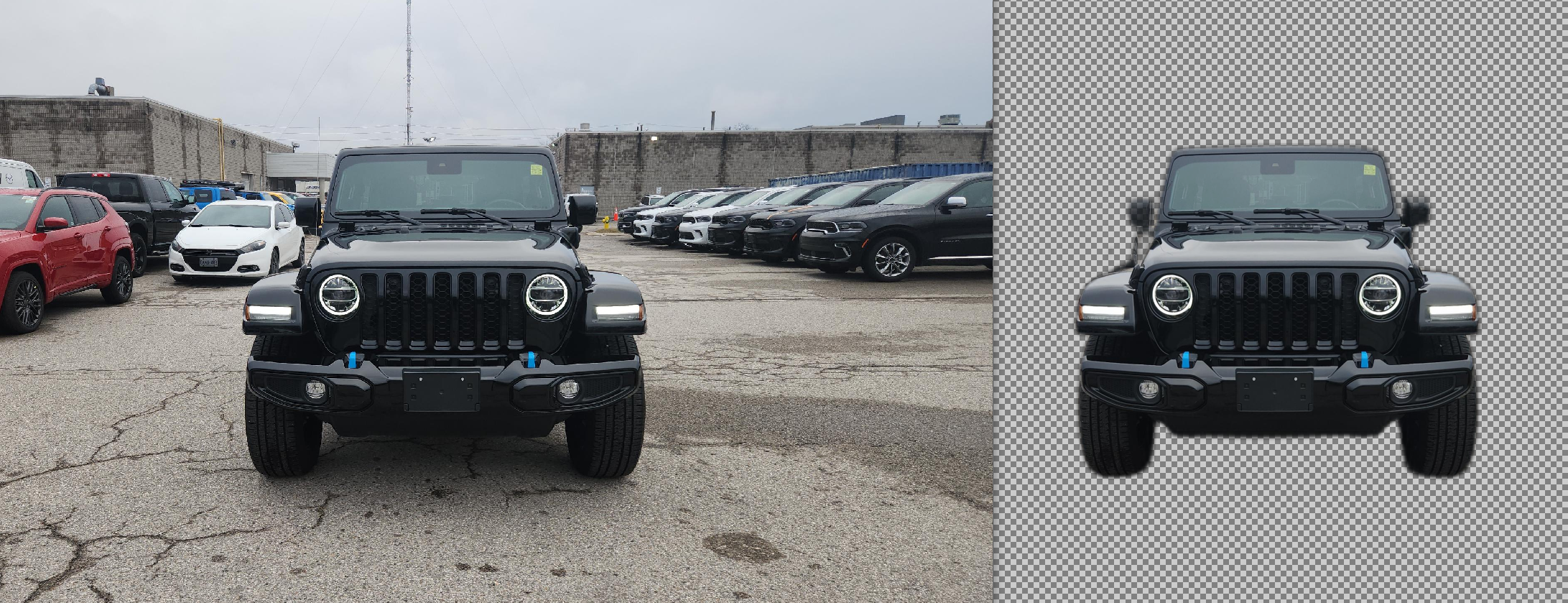

HTTP REQUEST VIA TOR NETWORK (DARKWEB)
curl 'https://api.ipify.org?format=txt'
The command above will send the request directly to the “clear” Internet, while the following will send via Tor:
curl -x socks5h://127.0.0.1:9050 'https://api.ipify.org?format=txt'
The key fact is the utilisation of a SOCKS5 Proxy. The same concept will be used in Python with the module requests.
Stem [Link] is the Python module capable of interacting with Tor’s ControlPort to gather metrics about the connection:
pip install stem
Edit the configuration of Tor:
sudo nano /etc/tor/torrc
Uncomment the following line to enable the ControlPort where you can get :
ControlPort 9051
Create a script with the following content:
#!/usr/bin/python3
import requests, time
from stem import Signal
from stem.control import Controller
# Set the headers for the request
headers = {'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/70.0.3538.102 Safari/537.36'}
PROXIES = {
'http': 'socks5://127.0.0.1:9050',
'https': 'socks5://127.0.0.1:9050'
}
# Initialize the controller for the Tor network
with Controller.from_port(address='127.0.0.1', port=9051) as controller:
controller.authenticate()
url = 'https://api.ipify.org?format=txt'
print('Public IP used for the request:')
while True:
# Set the new IP address
controller.signal(Signal.NEWNYM)
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers, proxies=PROXIES)
print('IP:', str(response.content, 'utf-8'), '-', controller.get_info("traffic/read"), 'bytes received -', controller.get_info("traffic/written"), 'bytes sent.')
time.sleep(10)
Manually start tor in one terminal and leave it there running.
tor
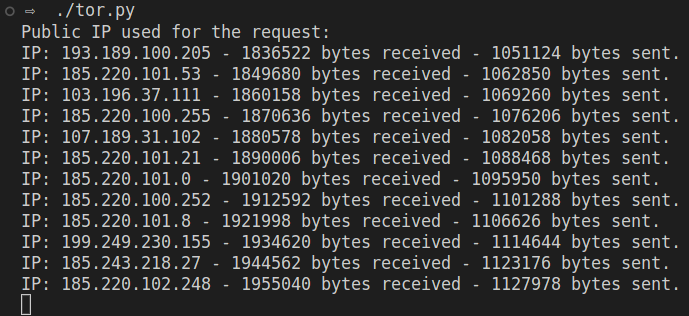
In another terminal, execute the created script. The expected output might reveal what Tor exit node’s IP was used to reach the “clear” Internet plus the total amount of bytes send and received.
EASY GRAPHIC USER INTERFACE
Install the dependent module:
sudo apt-get install python3-tk -y pip install easygui
Create a script with the following content:
#!/usr/bin/python3
import easygui
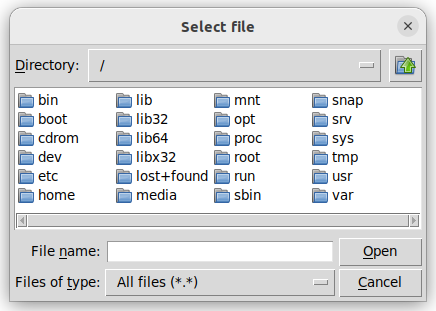
read_file_path = easygui.fileopenbox(title='Select file')
write_file_path = easygui.filesavebox(title='Save file to...')
prompt_question = easygui.ynbox('Continue?', 'Titlebox', ('Yes', 'No'))
message_box = easygui.msgbox('This is a basic message box.', 'Title Goes Here')
selected_option = easygui.buttonbox('Survey', 'Question', ('Answer 1', 'Answer 2', 'Answer 3'))
You might encounter the following pop-up windows. They might look a bit different depending on the operating system or graphic environment.
ARGUMENT PARSING
When executing an application it is very common to pass arguments in a certain order and use them by the index of each argument’s order.
The library argparse takes care of received arguments in any order, checking for type, assigning default values, and helping the user with a help menu.
- Optional
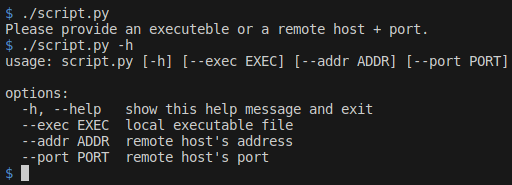
#!/usr/bin/python3
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--exec', type=str, help="local executable file")
parser.add_argument('--addr', type=str, help="remote host's address")
parser.add_argument('--port', type=int, help="remote host's port")
args = parser.parse_args()
if args.exec != None:
print('Execute:', args.exec)
elif args.addr != None and args.port != None:
print('Connect to:', args.host, 'on port:', args.port)
else:
print('Please provide an executeble or a remote host + port.')
- Positional
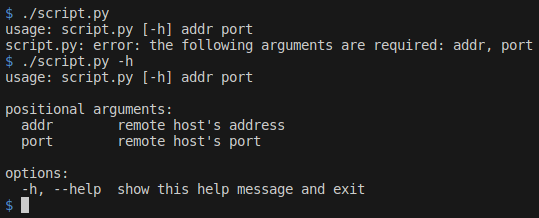
#!/usr/bin/python3
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('addr', type=str, help="remote host's address")
parser.add_argument('port', type=int, help="remote host's port")
args = parser.parse_args()
print('Connect to:', args.host, 'on port:', args.port)
- Multiple Arguments
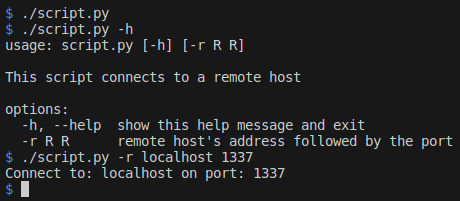
#!/usr/bin/python3
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="This script connects to a remote host")
parser.add_argument('-r', type=str, nargs=2, help="remote host's address followed by the port")
args = parser.parse_args()
if args.r is not None:
print('Connect to:', args.r[0], 'on port:', args.r[1])
More available options
- required=True
- make an argument mandatory.
- default=0
- sets a default values if not provided.
- nargs=’*’
- allows any number or arguments.
- choices=[‘local’, ‘remote’]
- limits the possible values.
- action=’store_true’
- makes an argument a boolean flag set to false if not set.
PRETTY PRINT
The pprint module provides a “pretty-print” of data structures like objects, arrays, and dictionaries.
from pprint import *
object = {"object":'chair',"quantity":2,"colors": ["red", "white", "blue"]}
pprint(object, depth=1, width=10)