OpenWrt [Link] was originally created as an open-source lightweight firmware for embedded devices such as routers and network-attached storage devices.
Running OpenWrt in a container (such as LXC) can provide several benefits:
- It allows for better resource isolation and management,
- Share the kernel with the host for an optimal use of resources,
- It can be easily backup, migrated, and cloned,
- The containerization isolates the firmware from the host system and its guests.
Proxmox is an open-source hypervisor capable of managing containers much like virtual machines, making it the best foundation for virtualizing OpenWrt.
This post will walk through the process of installing OpenWRT as a container (CT) in Proxmox. See more about Proxmox at [Link] and a cheat-sheet at [Link].
DOWNLOADING LXC TEMPLATE
Navigate to https://us.lxd.images.canonical.com/images/openwrt/ and find the latest buid, for example …/22.03/amd64/default/20230121_11:58/rootfs.tar.xz.
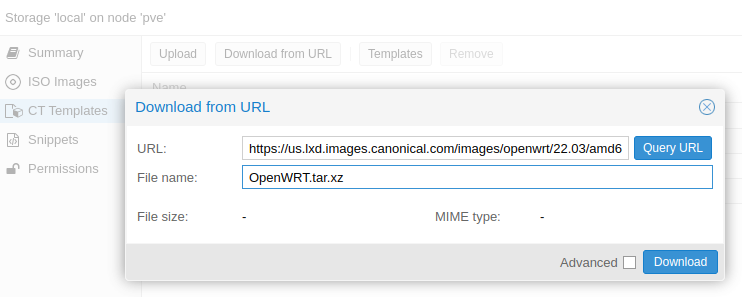
INSTALLING VIA CLI
Open the shell of the Proxmox host and issue the following command, customizing it as needed:
ct create 999 /var/lib/vz/template/cache/OpenWRT.tar.xz --arch amd64 --hostname OpenWrt --rootfs local-lvm:999 --memory 1024 --cores 2 --ostype unmanaged --unprivileged 1
The container number has to be unique and select a storage that contains at least 30 GB.
CONFIGURING CONTAINER’S NETWORKS
The container will need at least 2 network interfaces from the Host.
By default, the bridge interface vmbr0 is created during the installation. If needed, create a second Linux Bridge interface as follows:
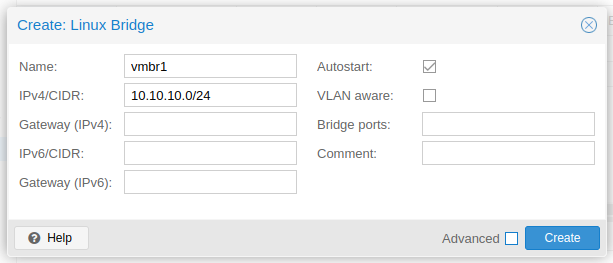
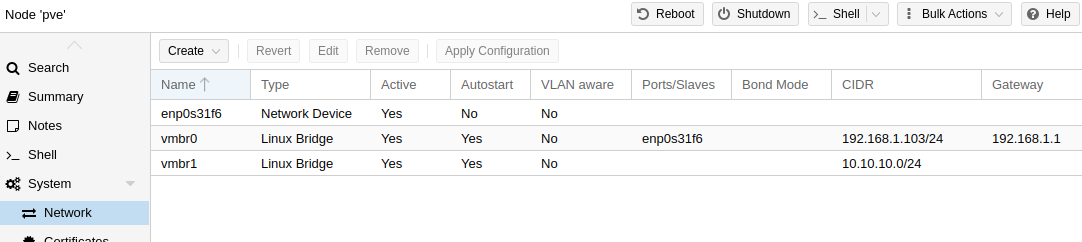
On the container’s network configuration both bridge networks need to be added:
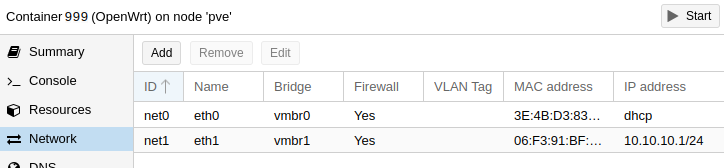
The container can be started now.
BASIC SYSTEM AND FIREWALL CONFIGURATION
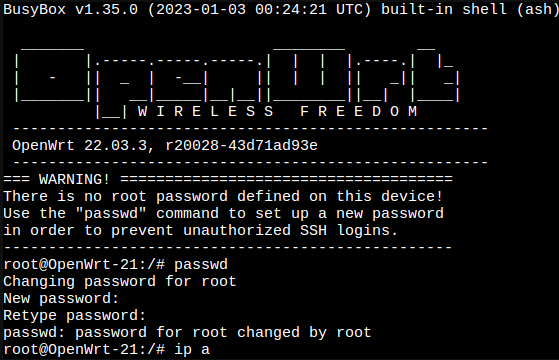
Open the console of the container and immediately change root password:
passwd
Then, check the IP assigned to the WAN interface eth0.
ip a
Edit the firewall configuration:
vim /etc/config/firewall
And add the following lines right after the block “Allow-Ping”.
config rule
option name LUCI-on-WAN
option src wan
option proto tcp
option family ipv4
option dest_port 80
option target ACCEPT
The reload the firewall configuration to apply the changes:
/etc/init.d/firewall reload
ACCESSING THE WEB-UI LUCI
Navigate to http://192.168.1.180.
Go to Network > Interfaces > “Add new interface…”
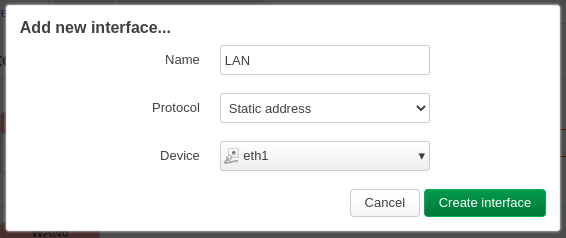
On the General Settings tab, set the IP 10.10.10.1 and mask 255.255.255.0.
On the Firewall Settings tab, select the zone “lan“.
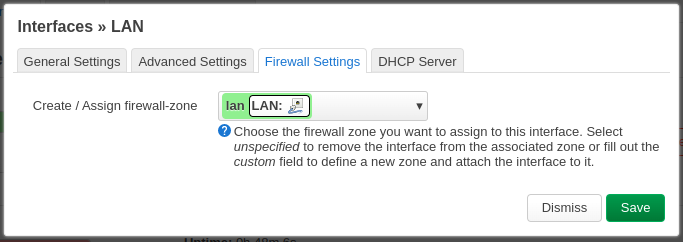
Enable the DHCP server, and then “Save“.
Optionally, remove WAN6 if it is not needed.
Click on “Save & Apply“. It will take few seconds to reload the router (OpenWRT).
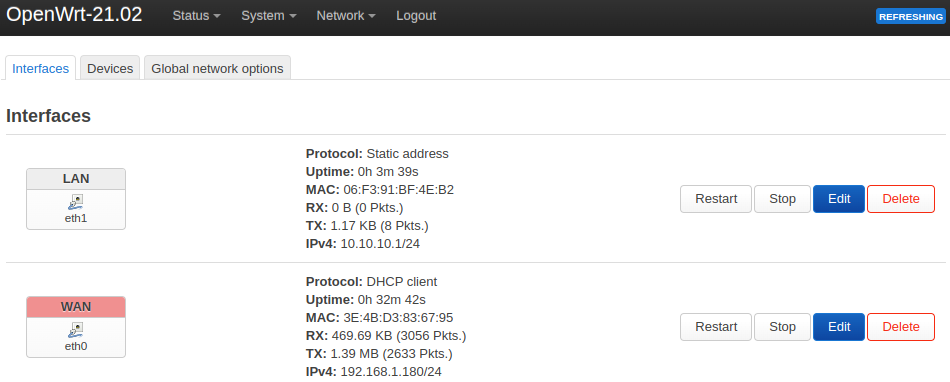
CONCLUSION
By attaching virtual machine and containers to the vmbr1 interface, they will all be isolated and protected by the OpenWRT router and its firewall rules.
BONUS OPENVPN CLIENT AND SERVER
Connect to the OpwnWRT CT via SSH or the Console, the issue:
opkg update opkg install luci-app-openvpn openvpn-openssl
Over the web-ui, refresh it and a new option on the top menu will appear “VPN“:
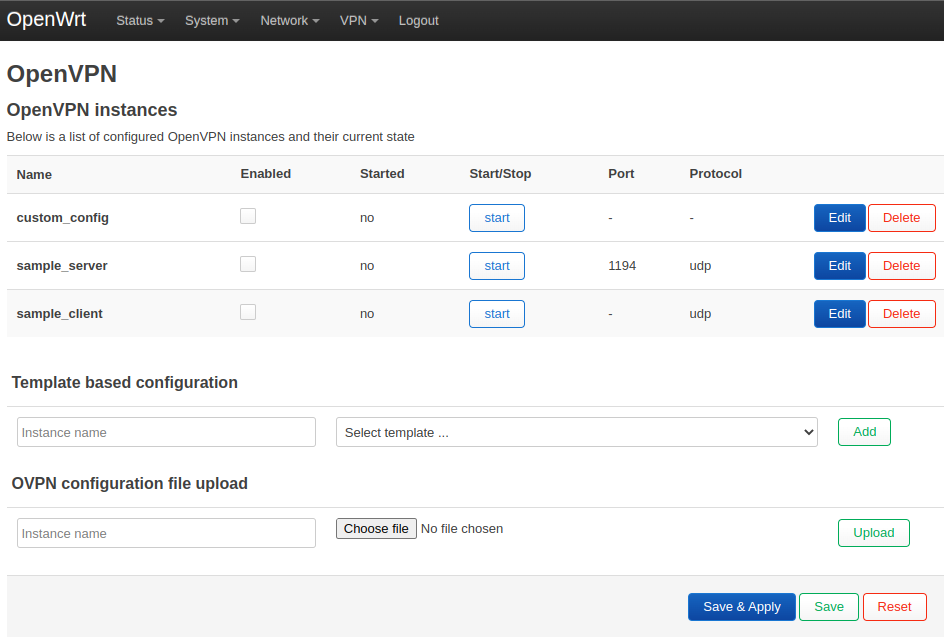
Configure and enable your VPN parameters. It won’t work out-of-the-box. Shutdown the CT and connect to the Proxmox host via SSH or the Console to make changes to the CT configuration.
nano /etc/pve/lxc/103.conf
Do the necessary adjustments to incorporate the highlighted configuration parameters:
arch: amd64 cores: 2 features: nesting=1 hostname: OpenWrt memory: 1024 net0: name=eth0,bridge=vmbr0,firewall=1,hwaddr=3E:4B:D3:83:67:95,ip=dhcp,type=veth net1: name=eth1,bridge=vmbr1,firewall=1,hwaddr=06:F3:91:BF:4E:B2,ip=10.10.10.1/24,type=veth ostype: unmanaged rootfs: Storage:103/vm-103-disk-0.raw,size=103G swap: 512 unprivileged: 1 lxc.cgroup2.devices.allow: c 10:200 rwm lxc.mount.entry: /dev/net dev/net none bind,create=dir
Then, allow unprivileged containers to be able to access the host’s virtual network resources (see the before and after), then start the CT again:
ls -l /dev/net/tun chown 100000:100000 /dev/net/tun ls -l /dev/net/tun pct start 103
On the Console of the CT, check if any new interface show up (“tun0“):
ip a
The VPN tunnel might be up and running and from the OpenWrt server it will be usable, but all the clients on the LAN side will not have access to the itnernet anymore.
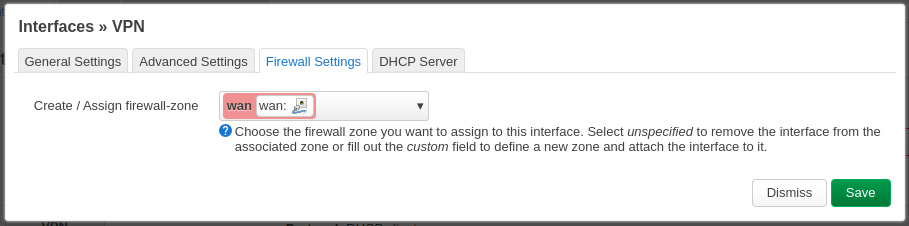
Back to the web-ui, go to Network > Interfaces > “Ass new interface…”
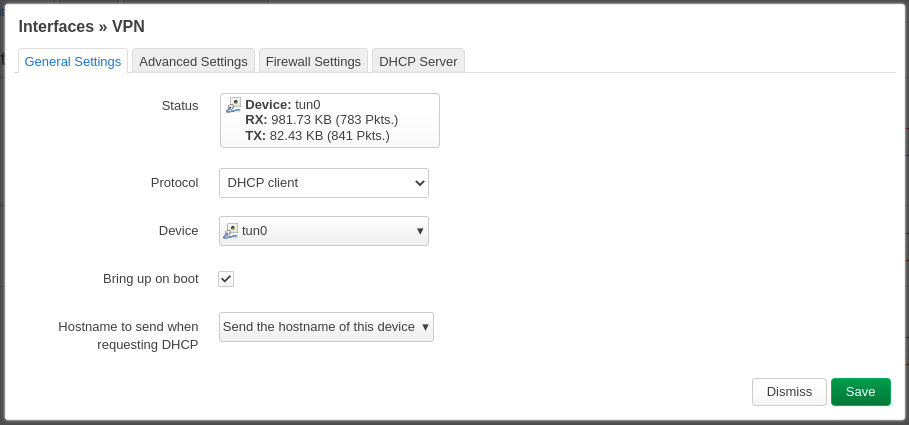
Edit the net interface and on the tab Firewall Settings, assign firewall-zone WAN.
Ping anywhere on the internet to test connectivity. Also test for domain resolution. If your OpenVPN configuration uses “block-outside-dns”, any DNS query outside the tunnel will be blocked to prevent leaks. Consider using a custom DNS server instead.