In the first look at the diagram above, there is no need for the Router R1 to the computers to be able to talk to each other. But the network is segmented in VLANs.
You can read what is and how VLAN works in this other post [Read It].
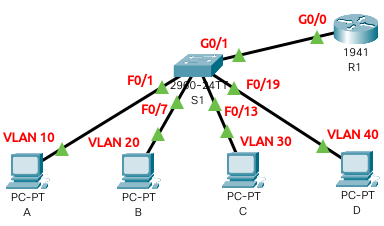
Switch configuration:
interface GigabitEthernet0/1 switchport mode trunk interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport access vlan 10 switchport mode access interface FastEthernet0/7 switchport access vlan 20 switchport mode access interface FastEthernet0/13 switchport access vlan 30 switchport mode access interface FastEthernet0/19 switchport access vlan 40 switchport mode access
Router configuration:
int g0/0 no shut int g0/0.10 encapsulation dot1q 10 ip add 172.17.7.1 255.255.255.192 int g0/0.20 encapsulation dot1q 20 ip add 172.17.7.65 255.255.255.192 int g0/0.30 encapsulation dot1q 30 ip add 172.17.7.129 255.255.255.192 int g0/0.40 encapsulation dot1q 40 ip add 172.17.7.193 255.255.255.192 service dhcp ip dhcp pool POOL10 network 172.17.7.0 255.255.255.192 default-router 172.17.7.1 dns-server 172.17.7.1 ip dhcp excluded-address 172.17.7.1 ip dhcp pool POOL20 network 172.17.7.64 255.255.255.192 default-router 172.17.7.65 dns-server 172.17.7.65 ip dhcp excluded-address 172.17.7.65 ip dhcp pool POOL30 network 172.17.7.128 255.255.255.192 default-router 172.17.7.129 dns-server 172.17.7.129 ip dhcp excluded-address 172.17.7.129 ip dhcp pool POOL40 network 172.17.7.192 255.255.255.192 default-router 172.17.7.193 dns-server 172.17.7.193 ip dhcp excluded-address 172.17.7.193
Useful commands for this exercise:
show ip dhcp binding show arp interface range f0/1-24 encapsulation dot1Q 1 native
Note: the last command informs the router when VLAN the frame belongs in case it comes with no dot1Q encapsulation. Replace 1 with the desired Native (default) VLAN.
Bonus: if there is a case where a router is between the client and the DHCP server, the router needs to be configured as DHCP Relay:
interface g0/0 ip helper-address 10.0.0.1
Replace 10.0.0.1 with the IP address of the DHCP Server.
The command ‘ip helper-address’ does not only relays DHCP but also other services too:
- Time (port 37)
- TACACS (port 49)
- DNS (port 53)
- BOOTP/DHCP Server (port 67)
- BOOTP/DHCP Client (port 68)
- TFTP (port 69)
- NetBIOS name service (port 137)
- NetBIOS datagram service (port 138)
You can define what will be forwarded (relayed) or not by using:
ip forward-protocol udp 37 no ip forward-protocol udp 53 ip directed-broadcast